Hyper Ige Syndrome Photograph by Mid Essex Hospital Services Nhs Trust/science Photo Library
Many different syndromes are known to lead to high levels of an antibody called immunoglobulin E, or IgE. Many more such syndromes likely remain unknown. Collectively, these conditions are called hyper-IgE syndromes, or HIES. Other conditions, such as severe eczema, can lead to extremely high IgE levels that are not caused by a syndrome at all.
Hyper IgE syndrome
Hyper-IgE syndrome is a hereditary combined B- and T-cell immunodeficiency characterized by recurrent staphylococcal abscesses of the skin, sinopulmonary infections, and severe pruritic eosinophilic dermatitis. Diagnosis is confirmed by measurement of serum IgE levels. Treatment consists of supportive measures, including lifelong prophylactic.

HyperIgE (Job syndrome) Medicine Keys for MRCPs
Most patients with hyper IgE syndrome are treated with long-term antibiotic therapy to prevent staphylococcal infections. Good skin care is also important in patients with hyper IgE syndrome. High-dose intravenous gamma-globulin has also been suggested for the treatment of severe eczema in patients with HIES and atopic dermatitis. History

Hyper IgE syndrome Mnemonic MEDizzy
Disease Overview. Hyper IgE syndromes (HIES) are rare primary immune deficiencies characterized by elevated serum IgE, skin inflammation (dermatitis) and recurrent skin and lung infections. There are two forms of HIES, which have the above characteristics in common but otherwise have distinct presentations, courses and outcomes: autosomal.
Hyper IgE syndrom (hyperimunoglobulin E syndrom) příznaky, projevy, symptomy Příznaky a
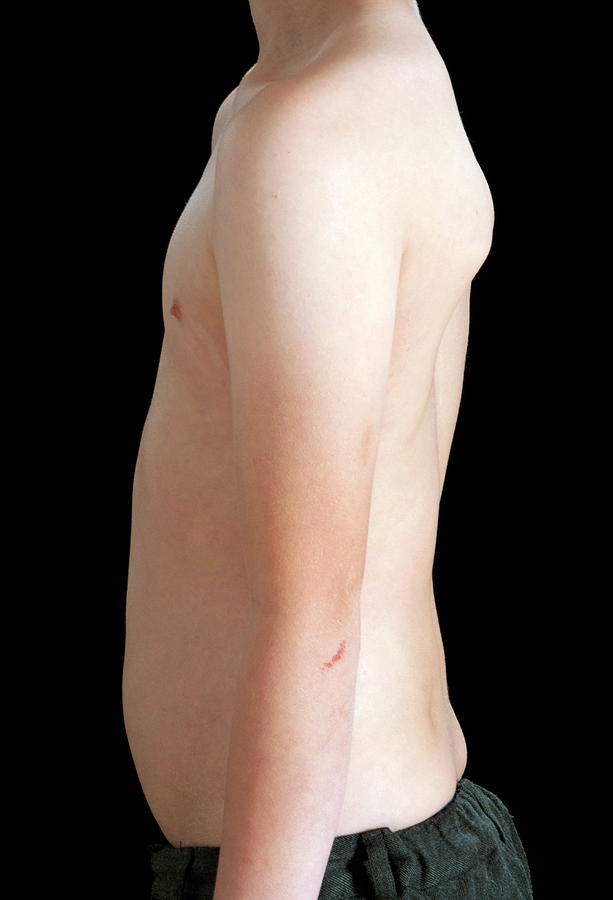
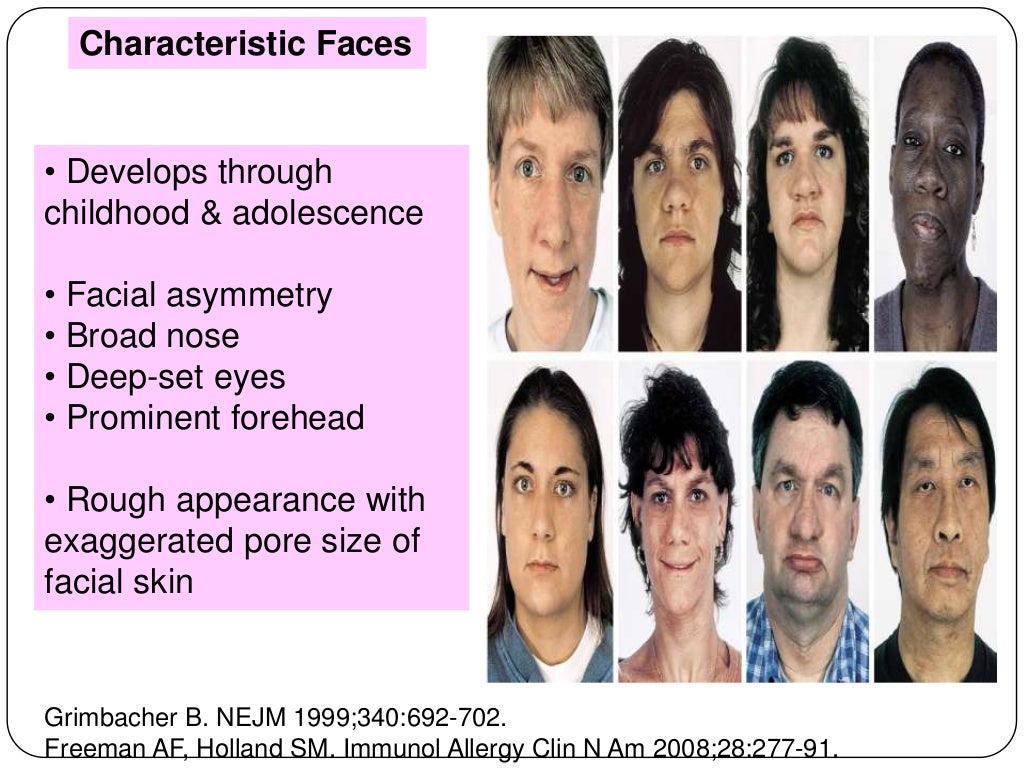
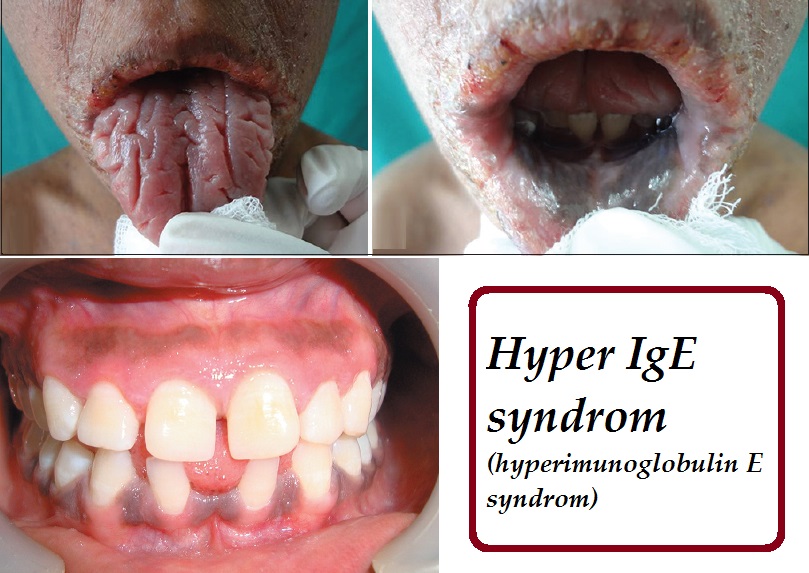
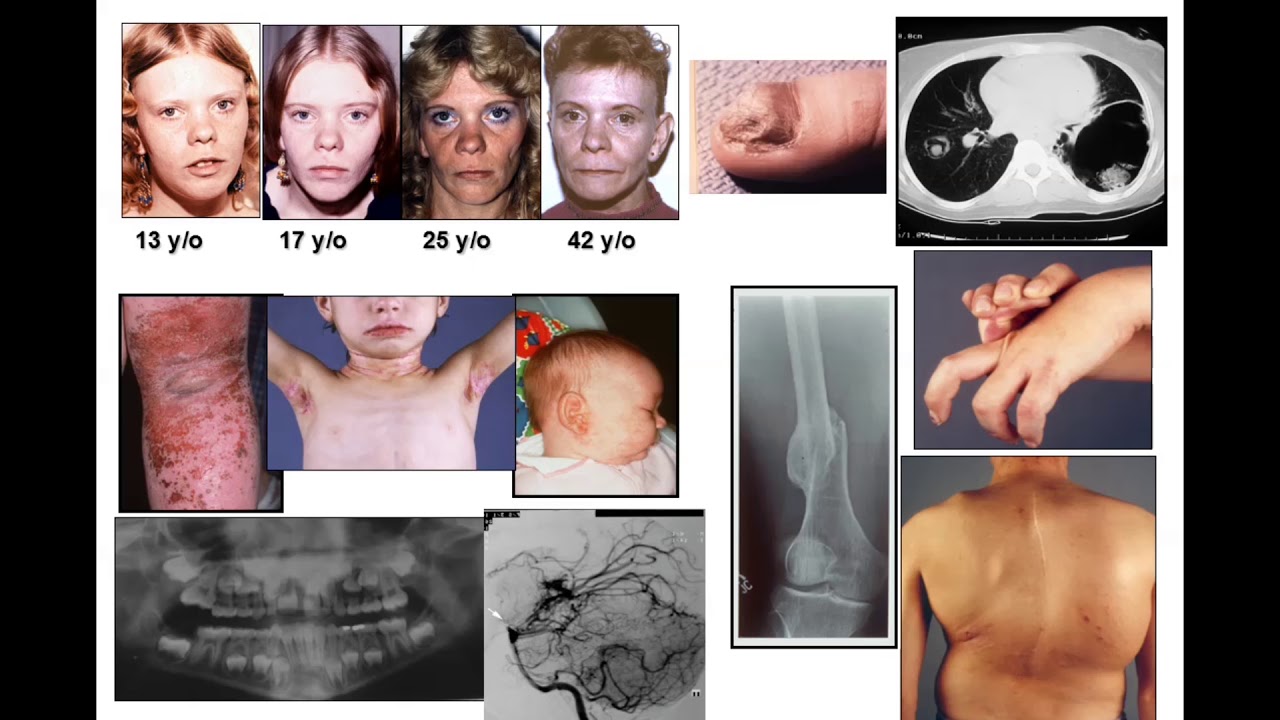
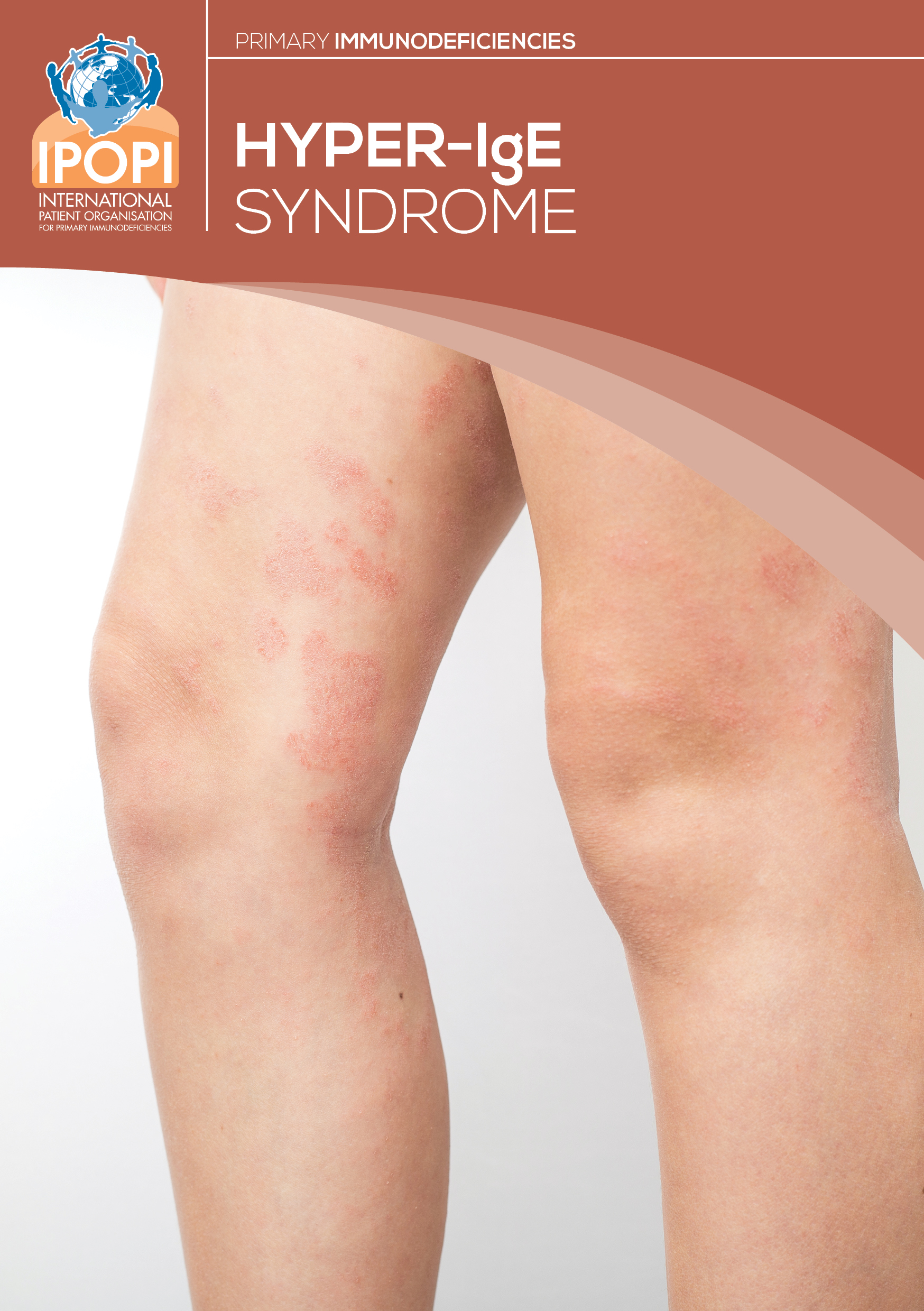
Hyper IgE syndrome (HIES) is a rare disorder characterized by eczema, recurrent infections of the skin and lungs, typically with Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans and certain viruses, and elevated levels of serum IgE. Other clinical manifestations include characteristic facies (prominent forehead, broad nasal bridge and facial asymmetry), chronic eczematous dermatitis, retained primary.

PPT Epidemiology & Risk Factors PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4357741
Hyper-IgE syndrome is a rare immunodeficiency disorder that causes recurrent infections, eczema, and high levels of IgE in the blood. This article reviews the clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of hyper-IgE syndrome, as well as the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis. Read more to learn about this challenging condition and the latest advances in research.

Hyper IgE syndrome (Job's syndrome ) Immunodeficiency disorder clinical features YouTube
The hyper-IgE syndrome with recurrent infections is a rare immunodeficiency characterized by recurrent skin and pulmonary abscesses and extremely elevated levels of IgE in serum. Associated facial.

Dermatitis and the Newborn Rash of HyperIgE Syndrome Dermatology JAMA Dermatology JAMA
Hyper-IgE syndrome (HIES) is first described by Davis and Wedgwood in 1966, in two girls suffering from recurrent cold staphylococcal abscesses, pneumonia, and neonatal-onset eczema.1 As this original report predated the identification of IgE, 2 a high serum concentration of IgE level was not recognized at this point.
Hyper IgE Syndrome (HIES) YouTube
Abstract. The hyper-IgE syndromes (HIES; originally named Job's syndrome) are a collection of primary immunodeficiency syndromes resulting in elevated serum IgE levels and typified by recurrent staphylococcal skin abscesses, eczema and pulmonary infections. The disorder has autosomal dominant and recessive forms.

Older patients with hyperIgE syndrome show thickened doughy texture of... Download Scientific
Hyper IgE syndrome (HIES), also known as Job syndrome, is a rare primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by elevated serum IgE levels, recurrent infections, and various clinical features. Early diagnosis, prompt management of infections, and supportive care are essential in improving outcomes for individuals with HIES..
HyperIgE Syndrome IPOPI
Hyper-IgE syndrome is caused by harmful genetic changes, also known as pathogenic variants. Genetic changes can occur randomly, as a result of environmental factors, from parents passing them down to their children, or a combination of these. Additionally, they can occur before birth or at any time during a person's life.

Eczematous Dermatitis in the Setting of HyperIgE Syndrome Successfully Treated With Omalizumab
Description. Autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome (AD-HIES), formerly known as Job syndrome, is a condition that affects several body systems, particularly the immune system. Recurrent infections are common in people with this condition. Affected individuals tend to have frequent bouts of pneumonia, which are caused by certain kinds of.

Failure of Dental Exfoliation in Patients with the HyperIgE Syndrome.... Download Scientific
Job Syndrome (Hyper-IgE syndrome) is a rare, primary immunodeficiency distinguished by the clinical triad of atopic dermatitis, recurrent skin staphylococcal infections, and recurrent pulmonary infections. The disease is characterized by elevated IgE levels with an early onset in primary childhood. This activity reviews the evaluation and.

Hyper IgE syndrome (Job Syndrome) Immunology USMLE Step 1 YouTube
Hyper-IgE syndrome is a hereditary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by recurring boils, sinus and lung infections, and a severe rash that appear during infancy. Levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE) are very high. In infants with hyper-IgE syndrome, abscesses form in the skin, joints, lungs, or other organs.

Which are the causes of Hyper IgE Syndrome?
10.1111/imcb.12209. Hyper IgE syndromes comprise a group of rare primary immunodeficiency disorders characterized by a triad of atopic dermatitis, recurrent skin and lung infections along with elevated IgE levels. Job syndrome or autosomal dominant hyper IgE syndrome because of heterozygous loss-of-function mutations with dominant negative.

What are the best treatments for Hyper IgE Syndrome?
Hyper IgE syndrome is an immune deficiency caused by a genetic mutation in either STAT3 (autosomal dominant, also known as Job's syndrome) or DOCK8 (autosomal recessive). There may be other mutations in other genes that are not known at this time. Patients with either form of hyper IgE syndrome often have trouble fighting harmful bacteria and.